分类法/范例四: Classifier comparison
这个范例的主要目的
- 比较各种分类器
- 利用图示法观察各种分类器的分类边界及区域
(一)引入函式并准备分类器
- 将分类器引入之后存放入一个
list里 - 这边要注意 sklearn.discriminant_analysis 必需要
sklearn 0.17以上才能执行
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons, make_circles, make_classification
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, AdaBoostClassifier
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis
h = .02 # step size in the mesh
names = ["Nearest Neighbors", "Linear SVM", "RBF SVM", "Decision Tree",
"Random Forest", "AdaBoost", "Naive Bayes", "Linear Discriminant Ana.",
"Quadratic Discriminant Ana."]
classifiers = [
KNeighborsClassifier(3),
SVC(kernel="linear", C=0.025),
SVC(gamma=2, C=1),
DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=5),
RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=5, n_estimators=10, max_features=1),
AdaBoostClassifier(),
GaussianNB(),
LinearDiscriminantAnalysis(),
QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis()]
(二)准备测试资料
- 利用
make_classification产生分类资料,n_features=2表示共有两个特徵,n_informative=2代表有两个类别 - 所产生之 X: 100 x 2矩阵,y: 100 元素之向量,y的数值仅有0或是1用来代表两种类别
- 利用
X += 2 * rng.uniform(size=X.shape)加入适度的杂讯后将(X,y)资料集命名为linear_separable - 最后利用
make_moon()及make_circles()产生空间中月亮形状及圆形之数据分佈后,一併存入datasets变数
X, y = make_classification(n_features=2, n_redundant=0, n_informative=2,
random_state=1, n_clusters_per_class=1)
rng = np.random.RandomState(2)
X += 2 * rng.uniform(size=X.shape)
linearly_separable = (X, y)
datasets = [make_moons(noise=0.3, random_state=0),
make_circles(noise=0.2, factor=0.5, random_state=1),
linearly_separable
]
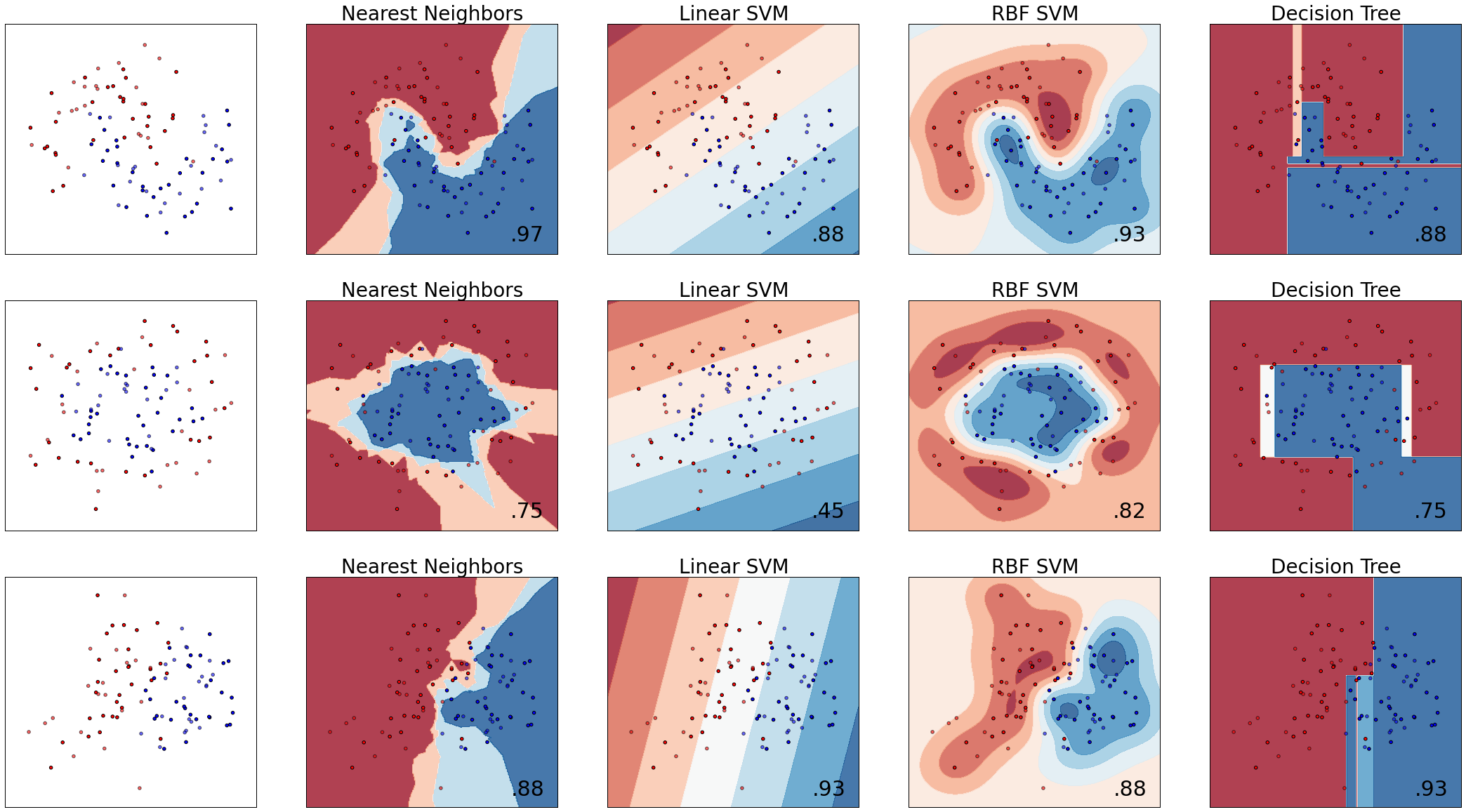
(三)测试分类器并作图
接下来这段程式码有两个for 迴圈,外迴圈走过三个的dataset,内迴圈则走过所有的分类器。 为求简要说明,我们将程式码简略如下:
- 外迴圈:资料迴圈。首先画出资料分佈,接著将资料传入分类器迴圈
for ds in datasets: X, y = ds #调整特徵值大小使其在特定范围 X = StandardScaler().fit_transform(X) #利用train_test_split将资料分成训练集以及测试集 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=.4) #产生资料网格来大范围测试分类器,范例EX 3有详述该用法 xx, yy = np.meshgrid(..........省略) # 画出训练资料点 ax.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c=y_train, cmap=cm_bright) # 画出测试资料点,用alpha=0.6将测试资料点画的"淡"一些 ax.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c=y_test, cmap=cm_bright, alpha=0.6) 内迴圈:分类器迴圈。测试分类准确度并绘製分类边界及区域
for name, clf in zip(names, classifiers): clf.fit(X_train, y_train) score = clf.score(X_test, y_test) # Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will assign a color to each # point in the mesh [x_min, m_max]x[y_min, y_max]. if hasattr(clf, "decision_function"): Z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]) else: Z = clf.predict_proba(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])[:, 1] # Put the result into a color plot Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape) ax.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=cm, alpha=.8)为了显示方便,我将原始码的内圈改为
for name, clf in zip(names[0:4], classifiers[0:4]):只跑过前四个分类器。
%matplotlib inline
figure = plt.figure(figsize=(30,20), dpi=300)
i = 1
# iterate over datasets
for ds in datasets:
# preprocess dataset, split into training and test part
X, y = ds
X = StandardScaler().fit_transform(X)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=.4)
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - .5, X[:, 0].max() + .5
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - .5, X[:, 1].max() + .5
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
# just plot the dataset first
cm = plt.cm.RdBu
cm_bright = ListedColormap(['#FF0000', '#0000FF'])
ax = plt.subplot(len(datasets), (len(classifiers) + 1)//2, i)
# Plot the training points
ax.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c=y_train, cmap=cm_bright)
# and testing points
ax.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c=y_test, cmap=cm_bright, alpha=0.6)
ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
i += 1
# iterate over classifiers
for name, clf in zip(names[0:4], classifiers[0:4]):
ax = plt.subplot(len(datasets), (len(classifiers) + 1)//2, i)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
score = clf.score(X_test, y_test)
# Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will assign a color to each
# point in the mesh [x_min, m_max]x[y_min, y_max].
if hasattr(clf, "decision_function"):
Z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
else:
Z = clf.predict_proba(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])[:, 1]
# Put the result into a color plot
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
ax.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=cm, alpha=.8)
# Plot also the training points
ax.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c=y_train, cmap=cm_bright)
# and testing points
ax.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c=y_test, cmap=cm_bright,
alpha=0.6)
ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
ax.set_title(name,fontsize=28)
ax.text(xx.max() - .3, yy.min() + .3, ('%.2f' % score).lstrip('0'),
size=30, horizontalalignment='right')
i += 1
figure.subplots_adjust(left=.02, right=.98)
plt.show()
(四) 原始码列表
Python source code: plot_classifier_comparison.py
http://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/classification/plot_classifier_comparison.html
print(__doc__)
# Code source: Gaël Varoquaux
# Andreas Müller
# Modified for documentation by Jaques Grobler
# License: BSD 3 clause
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons, make_circles, make_classification
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, AdaBoostClassifier
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis
h = .02 # step size in the mesh
names = ["Nearest Neighbors", "Linear SVM", "RBF SVM", "Decision Tree",
"Random Forest", "AdaBoost", "Naive Bayes", "Linear Discriminant Analysis",
"Quadratic Discriminant Analysis"]
classifiers = [
KNeighborsClassifier(3),
SVC(kernel="linear", C=0.025),
SVC(gamma=2, C=1),
DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=5),
RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=5, n_estimators=10, max_features=1),
AdaBoostClassifier(),
GaussianNB(),
LinearDiscriminantAnalysis(),
QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis()]
X, y = make_classification(n_features=2, n_redundant=0, n_informative=2,
random_state=1, n_clusters_per_class=1)
rng = np.random.RandomState(2)
X += 2 * rng.uniform(size=X.shape)
linearly_separable = (X, y)
datasets = [make_moons(noise=0.3, random_state=0),
make_circles(noise=0.2, factor=0.5, random_state=1),
linearly_separable
]
figure = plt.figure(figsize=(27, 9))
i = 1
# iterate over datasets
for ds in datasets:
# preprocess dataset, split into training and test part
X, y = ds
X = StandardScaler().fit_transform(X)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=.4)
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - .5, X[:, 0].max() + .5
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - .5, X[:, 1].max() + .5
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
# just plot the dataset first
cm = plt.cm.RdBu
cm_bright = ListedColormap(['#FF0000', '#0000FF'])
ax = plt.subplot(len(datasets), len(classifiers) + 1, i)
# Plot the training points
ax.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c=y_train, cmap=cm_bright)
# and testing points
ax.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c=y_test, cmap=cm_bright, alpha=0.6)
ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
i += 1
# iterate over classifiers
for name, clf in zip(names, classifiers):
ax = plt.subplot(len(datasets), len(classifiers) + 1, i)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
score = clf.score(X_test, y_test)
# Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will assign a color to each
# point in the mesh [x_min, m_max]x[y_min, y_max].
if hasattr(clf, "decision_function"):
Z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
else:
Z = clf.predict_proba(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])[:, 1]
# Put the result into a color plot
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
ax.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=cm, alpha=.8)
# Plot also the training points
ax.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c=y_train, cmap=cm_bright)
# and testing points
ax.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c=y_test, cmap=cm_bright,
alpha=0.6)
ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
ax.set_title(name)
ax.text(xx.max() - .3, yy.min() + .3, ('%.2f' % score).lstrip('0'),
size=15, horizontalalignment='right')
i += 1
figure.subplots_adjust(left=.02, right=.98)
plt.show()