特徵选择/范例三: Recursive feature elimination with cross-validation
http://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/feature_selection/plot_rfe_with_cross_validation.html
REFCV比REF多一个交叉比对的分数(gridscores),代表选择多少特徵后的准确率。但REFCV不用像REF要给定选择多少特徵,而是会依照交叉比对的分数而自动选择训练的特徵数。
本范例示范RFE的进阶版,当我们在使用RFE指令时,需要输入训练特徵数目,让训练机能排除到其他较不具有影响力的特徵,也就是要有预期的训练特徵数目。在RFECV指令提供了使用交叉验证来选择有最好准确率的训练特徵数目。而交叉验证也可以帮助我们避免训练时造成过度训练(overfitting)的现象,也就是当我们从某一组资料中挑出一笔训练资料,能够对剩下的测试资料预测出准确度最好的分类,却发现这个分类机状态无法准确的辨识新进资料的结果,因为这个最佳状态只适用在特定的组合情况。因此使用RFECV后,我们可以从结果看出,使用多少特徵做分类判断可以得到的准确率高低。
- 以叠代方式计算模型
- 以交叉验证来取得影响力特徵
(一)建立模拟资料
# Build a classification task using 3 informative features
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=25, n_informative=3,
n_redundant=2, n_repeated=0, n_classes=8,
n_clusters_per_class=1, random_state=0)
说明可以参考EX1,执行过此函数后,我们可以得到具有25个特徵且有1000样本的资料,其中具有目标影响力的特徵有三个,有两个特徵是由具有资讯影响力的特徵线性组合出来的,而目标共有八个分类类别。
(二)以叠代排序特徵影响力,并以交叉验证来选出具有实际影响力的特徵
在使用RFECV指令前,需要建立支持向量机物件,以及交叉验证的形式。本范例仍使用SVC以及线性核函数来作为主要的分类机。
在交叉验证的部分,我们使用StratifiedKFold指令来做K 堆叠(Fold)的交叉验证。也就是将资料分为K堆,一堆作为预测用,剩下的(K-1)堆则用来训练,经过计算后,再以另外一堆作为预测,重複K次。
而scoring参数则是依照分类资料的形式,输入对应的评分方式。以本例子为超过两类型的分类,因此使用'accuracy'来对多重分类的评分方式。详细可参考scoring
# Create the RFE object and compute a cross-validated score.
svc = SVC(kernel="linear")
# The "accuracy" scoring is proportional to the number of correct
# classifications
rfecv = RFECV(estimator=svc, step=1, cv=StratifiedKFold(y, 2),
scoring='accuracy')
rfecv.fit(X, y)
print("Optimal number of features : %d" % rfecv.n_features_)
以RFECV设定好的功能物件,即可用以做训练的动作。其结果可由nfeatures得知有几样特徵是具有实际影响力。并可以由gridscores看出特徵的多寡如何影响准确率。 此功能需要设定交叉验证的形式,本范例是以交叉验证产生器做为输入,其功能介绍如下。
(三)画出具有影响力特徵对应准确率的图
下图的曲线表示选择多少个特徵来做训练,会得到多少的准确率。
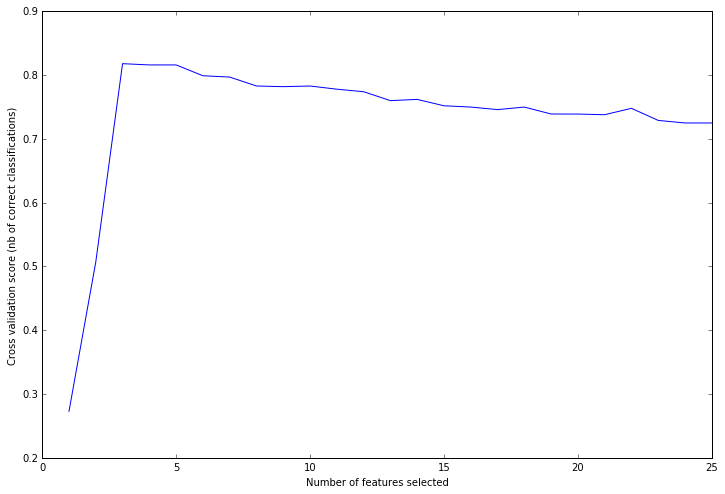
可以看到选择三个最具有影响力的特徵时,交叉验证的准确率高达81.8%。与建立模拟资料的n_informative=3是相对应的。
(四) 原始码出处
Python source code: plot_rfe_digits.py
print(__doc__)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.cross_validation import StratifiedKFold
from sklearn.feature_selection import RFECV
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
# Build a classification task using 3 informative features
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=25, n_informative=3,
n_redundant=2, n_repeated=0, n_classes=8,
n_clusters_per_class=1, random_state=0)
# Create the RFE object and compute a cross-validated score.
svc = SVC(kernel="linear")
# The "accuracy" scoring is proportional to the number of correct
# classifications
rfecv = RFECV(estimator=svc, step=1, cv=StratifiedKFold(y, 2),
scoring='accuracy')
rfecv.fit(X, y)
print("Optimal number of features : %d" % rfecv.n_features_)
# Plot number of features VS. cross-validation scores
plt.figure()
plt.xlabel("Number of features selected")
plt.ylabel("Cross validation score (nb of correct classifications)")
plt.plot(range(1, len(rfecv.grid_scores_) + 1), rfecv.grid_scores_)
plt.show()
本章介绍到函式用法
RFECV() 的参数
class sklearn.feature_selection.RFECV(estimator, step=1, cv=None, scoring=None, estimator_params=None, verbose=0)[source]
参数
- estimator
- step
- cv: 若无输入,预设为3-fold的交叉验证。输入整数i,则做i-fold交叉验证。若为物件,则以该物件做为交叉验证产生器。
- scoring
- estimator_params
- verbose
输出
- n_features_: 预测有影响力的特徵的总数目
- support_: 有影响力的特徵遮罩,可以用来挑出哪些特徵
- ranking_: 各特徵的影响力程度
- gridscores: 从最有影响力的特徵开始加入,计算使用多少个特徵对应得到的准确率。
- estimator_