分类法/范例五:Linear and Quadratic Discriminant Analysis with confidence ellipsoid
线性判别以及二次判别的比较
http://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/classification/plot_lda_qda.html
(一)资料产生function
这个范例引入的套件,主要特点在:
scipy.linalg:线性代数相关函式,这里主要使用到linalg.eigh 特徵值相关问题matplotlib.colors: 用来处理绘图时的色彩分佈LinearDiscriminantAnalysis:线性判别演算法QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis:二次判别演算法
%matplotlib inline
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
from matplotlib import colors
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis
接下来是设定一个线性变化的colormap,LinearSegmentedColormap(name, segmentdata) 预设会传回一个256个值的数值颜色对应关系。用一个具备有三个项目的dict变数segmentdata来设定。以'red': [(0, 1, 1), (1, 0.7, 0.7)]来解释,就是我们希望数值由0到1的过程,红色通道将由1线性变化至0.7。
cmap = colors.LinearSegmentedColormap(
'red_blue_classes',
{'red': [(0, 1, 1), (1, 0.7, 0.7)],
'green': [(0, 0.7, 0.7), (1, 0.7, 0.7)],
'blue': [(0, 0.7, 0.7), (1, 1, 1)]})
plt.cm.register_cmap(cmap=cmap)
我们可以用以下程式码来观察。当输入数值为np.arange(0,1.1,0.1)也就是0,0.1...,1.0 时RGB数值的变化情形。
values = np.arange(0,1.1,0.1)
cmap_values = mpl.cm.get_cmap('red_blue_classes')(values)
import pandas as pd
pd.set_option('precision',2)
df=pd.DataFrame(np.hstack((values.reshape(11,1),cmap_values)))
df.columns = ['Value', 'R', 'G', 'B', 'Alpha']
print(df)
Value R G B Alpha
0 0.0 1.0 0.7 0.7 1
1 0.1 1.0 0.7 0.7 1
2 0.2 0.9 0.7 0.8 1
3 0.3 0.9 0.7 0.8 1
4 0.4 0.9 0.7 0.8 1
5 0.5 0.8 0.7 0.9 1
6 0.6 0.8 0.7 0.9 1
7 0.7 0.8 0.7 0.9 1
8 0.8 0.8 0.7 0.9 1
9 0.9 0.7 0.7 1.0 1
10 1.0 0.7 0.7 1.0 1
接著我们产生两组资料, 每组资料有 600笔资料,2个特徵 X: 600x2以及2个类别 y:600 (前300个元素为0,馀下为1):
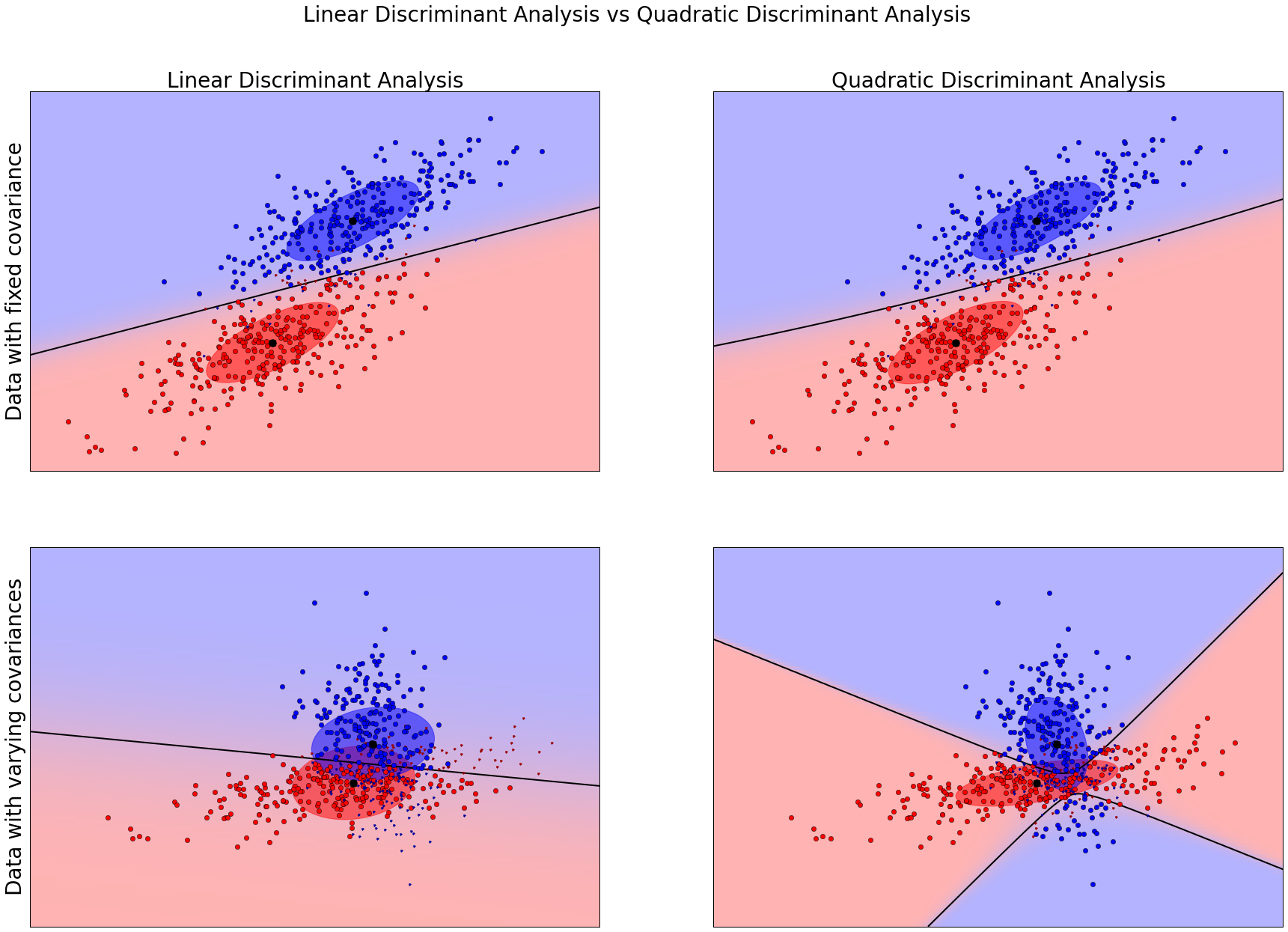
dataset_fixed_cov():2个类别的特徵具备有相同共变数(covariance)dataset_fixed_cov():2个类别的特徵具备有不同之共变数 差异落在X资料的产生np.dot(np.random.randn(n, dim), C)与np.dot(np.random.randn(n, dim), C.T)的不同。np.dot(np.random.randn(n, dim), C)会产生300x2之矩阵,其乱数产生的范围可交由C矩阵来控制。在dataset_fixed_cov()中,前后300笔资料产生之范围皆由C来调控。我们可以在最下方的结果图示看到上排影像(相同共变数)的资料分佈无论是红色(代表类别1)以及蓝色(代表类别2)其分佈形状相似。而下排影像(不同共变数),分佈形状则不同。图示中,横轴及纵轴分别表示第一及第二个特徵,读者可以试著将0.83这个数字减少或是将C.T改成C,看看最后结果图形有了什麽改变?
def dataset_fixed_cov():
'''Generate 2 Gaussians samples with the same covariance matrix'''
n, dim = 300, 2
np.random.seed(0)
C = np.array([[0., -0.23], [0.83, .23]])
X = np.r_[np.dot(np.random.randn(n, dim), C),
np.dot(np.random.randn(n, dim), C) + np.array([1, 1])] #利用 + np.array([1, 1]) 产生类别间的差异
y = np.hstack((np.zeros(n), np.ones(n))) #产生300个零及300个1并连接起来
return X, y
def dataset_cov():
'''Generate 2 Gaussians samples with different covariance matrices'''
n, dim = 300, 2
np.random.seed(0)
C = np.array([[0., -1.], [2.5, .7]]) * 2.
X = np.r_[np.dot(np.random.randn(n, dim), C),
np.dot(np.random.randn(n, dim), C.T) + np.array([1, 4])]
y = np.hstack((np.zeros(n), np.ones(n)))
return X, y
(二)绘图函式
- 找出 True Positive及False Negative 之辨认点
- 以红色及蓝色分别表示分类为 0及1的资料点,而以深红跟深蓝来表示误判资料
- 以
lda.predict_proba()画出分类的机率分佈(请参考范例三)
(为了方便在ipython notebook环境下显示,下面函式有经过微调)
def plot_data(lda, X, y, y_pred, fig_index):
splot = plt.subplot(2, 2, fig_index)
if fig_index == 1:
plt.title('Linear Discriminant Analysis',fontsize=28)
plt.ylabel('Data with fixed covariance',fontsize=28)
elif fig_index == 2:
plt.title('Quadratic Discriminant Analysis',fontsize=28)
elif fig_index == 3:
plt.ylabel('Data with varying covariances',fontsize=28)
# 步骤一:找出 True Positive及False postive 之辨认点
tp = (y == y_pred) # True Positive
tp0, tp1 = tp[y == 0], tp[y == 1] #tp0 代表分类为0且列为 True Positive之资料点
X0, X1 = X[y == 0], X[y == 1]
X0_tp, X0_fp = X0[tp0], X0[~tp0]
X1_tp, X1_fp = X1[tp1], X1[~tp1]
# 步骤二:以红蓝来画出分类资料,以深红跟深蓝来表示误判资料
# class 0: dots
plt.plot(X0_tp[:, 0], X0_tp[:, 1], 'o', color='red')
plt.plot(X0_fp[:, 0], X0_fp[:, 1], '.', color='#990000') # dark red
# class 1: dots
plt.plot(X1_tp[:, 0], X1_tp[:, 1], 'o', color='blue')
plt.plot(X1_fp[:, 0], X1_fp[:, 1], '.', color='#000099') # dark blue
#步骤三:画出分类的机率分佈(请参考范例三)
# class 0 and 1 : areas
nx, ny = 200, 100
x_min, x_max = plt.xlim()
y_min, y_max = plt.ylim()
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(x_min, x_max, nx),
np.linspace(y_min, y_max, ny))
Z = lda.predict_proba(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z[:, 1].reshape(xx.shape)
plt.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z, cmap='red_blue_classes',
norm=colors.Normalize(0., 1.))
plt.contour(xx, yy, Z, [0.5], linewidths=2., colors='k')
# means
plt.plot(lda.means_[0][0], lda.means_[0][1],
'o', color='black', markersize=10)
plt.plot(lda.means_[1][0], lda.means_[1][1],
'o', color='black', markersize=10)
return splot
def plot_ellipse(splot, mean, cov, color):
v, w = linalg.eigh(cov)
u = w[0] / linalg.norm(w[0])
angle = np.arctan(u[1] / u[0])
angle = 180 * angle / np.pi # convert to degrees
# filled Gaussian at 2 standard deviation
ell = mpl.patches.Ellipse(mean, 2 * v[0] ** 0.5, 2 * v[1] ** 0.5,
180 + angle, color=color)
ell.set_clip_box(splot.bbox)
ell.set_alpha(0.5)
splot.add_artist(ell)
splot.set_xticks(())
splot.set_yticks(())
(三)测试资料并绘图
def plot_lda_cov(lda, splot):
plot_ellipse(splot, lda.means_[0], lda.covariance_, 'red')
plot_ellipse(splot, lda.means_[1], lda.covariance_, 'blue')
def plot_qda_cov(qda, splot):
plot_ellipse(splot, qda.means_[0], qda.covariances_[0], 'red')
plot_ellipse(splot, qda.means_[1], qda.covariances_[1], 'blue')
###############################################################################
figure = plt.figure(figsize=(30,20), dpi=300)
for i, (X, y) in enumerate([dataset_fixed_cov(), dataset_cov()]):
# Linear Discriminant Analysis
lda = LinearDiscriminantAnalysis(solver="svd", store_covariance=True)
y_pred = lda.fit(X, y).predict(X)
splot = plot_data(lda, X, y, y_pred, fig_index=2 * i + 1)
plot_lda_cov(lda, splot)
plt.axis('tight')
# Quadratic Discriminant Analysis
qda = QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis(store_covariances=True)
y_pred = qda.fit(X, y).predict(X)
splot = plot_data(qda, X, y, y_pred, fig_index=2 * i + 2)
plot_qda_cov(qda, splot)
plt.axis('tight')
plt.suptitle('Linear Discriminant Analysis vs Quadratic Discriminant Analysis',fontsize=28)
plt.show()
Python source code: plot_lda_qda.py
http://scikit-learn.org/stable/_downloads/plot_lda_qda.py
print(__doc__)
from scipy import linalg
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
from matplotlib import colors
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis
###############################################################################
# colormap
cmap = colors.LinearSegmentedColormap(
'red_blue_classes',
{'red': [(0, 1, 1), (1, 0.7, 0.7)],
'green': [(0, 0.7, 0.7), (1, 0.7, 0.7)],
'blue': [(0, 0.7, 0.7), (1, 1, 1)]})
plt.cm.register_cmap(cmap=cmap)
###############################################################################
# generate datasets
def dataset_fixed_cov():
'''Generate 2 Gaussians samples with the same covariance matrix'''
n, dim = 300, 2
np.random.seed(0)
C = np.array([[0., -0.23], [0.83, .23]])
X = np.r_[np.dot(np.random.randn(n, dim), C),
np.dot(np.random.randn(n, dim), C) + np.array([1, 1])]
y = np.hstack((np.zeros(n), np.ones(n)))
return X, y
def dataset_cov():
'''Generate 2 Gaussians samples with different covariance matrices'''
n, dim = 300, 2
np.random.seed(0)
C = np.array([[0., -1.], [2.5, .7]]) * 2.
X = np.r_[np.dot(np.random.randn(n, dim), C),
np.dot(np.random.randn(n, dim), C.T) + np.array([1, 4])]
y = np.hstack((np.zeros(n), np.ones(n)))
return X, y
###############################################################################
# plot functions
def plot_data(lda, X, y, y_pred, fig_index):
splot = plt.subplot(2, 2, fig_index)
if fig_index == 1:
plt.title('Linear Discriminant Analysis')
plt.ylabel('Data with fixed covariance')
elif fig_index == 2:
plt.title('Quadratic Discriminant Analysis')
elif fig_index == 3:
plt.ylabel('Data with varying covariances')
tp = (y == y_pred) # True Positive
tp0, tp1 = tp[y == 0], tp[y == 1]
X0, X1 = X[y == 0], X[y == 1]
X0_tp, X0_fp = X0[tp0], X0[~tp0]
X1_tp, X1_fp = X1[tp1], X1[~tp1]
# class 0: dots
plt.plot(X0_tp[:, 0], X0_tp[:, 1], 'o', color='red')
plt.plot(X0_fp[:, 0], X0_fp[:, 1], '.', color='#990000') # dark red
# class 1: dots
plt.plot(X1_tp[:, 0], X1_tp[:, 1], 'o', color='blue')
plt.plot(X1_fp[:, 0], X1_fp[:, 1], '.', color='#000099') # dark blue
# class 0 and 1 : areas
nx, ny = 200, 100
x_min, x_max = plt.xlim()
y_min, y_max = plt.ylim()
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(x_min, x_max, nx),
np.linspace(y_min, y_max, ny))
Z = lda.predict_proba(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z[:, 1].reshape(xx.shape)
plt.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z, cmap='red_blue_classes',
norm=colors.Normalize(0., 1.))
plt.contour(xx, yy, Z, [0.5], linewidths=2., colors='k')
# means
plt.plot(lda.means_[0][0], lda.means_[0][1],
'o', color='black', markersize=10)
plt.plot(lda.means_[1][0], lda.means_[1][1],
'o', color='black', markersize=10)
return splot
def plot_ellipse(splot, mean, cov, color):
v, w = linalg.eigh(cov)
u = w[0] / linalg.norm(w[0])
angle = np.arctan(u[1] / u[0])
angle = 180 * angle / np.pi # convert to degrees
# filled Gaussian at 2 standard deviation
ell = mpl.patches.Ellipse(mean, 2 * v[0] ** 0.5, 2 * v[1] ** 0.5,
180 + angle, color=color)
ell.set_clip_box(splot.bbox)
ell.set_alpha(0.5)
splot.add_artist(ell)
splot.set_xticks(())
splot.set_yticks(())
def plot_lda_cov(lda, splot):
plot_ellipse(splot, lda.means_[0], lda.covariance_, 'red')
plot_ellipse(splot, lda.means_[1], lda.covariance_, 'blue')
def plot_qda_cov(qda, splot):
plot_ellipse(splot, qda.means_[0], qda.covariances_[0], 'red')
plot_ellipse(splot, qda.means_[1], qda.covariances_[1], 'blue')
###############################################################################
for i, (X, y) in enumerate([dataset_fixed_cov(), dataset_cov()]):
# Linear Discriminant Analysis
lda = LinearDiscriminantAnalysis(solver="svd", store_covariance=True)
y_pred = lda.fit(X, y).predict(X)
splot = plot_data(lda, X, y, y_pred, fig_index=2 * i + 1)
plot_lda_cov(lda, splot)
plt.axis('tight')
# Quadratic Discriminant Analysis
qda = QuadraticDiscriminantAnalysis(store_covariances=True)
y_pred = qda.fit(X, y).predict(X)
splot = plot_data(qda, X, y, y_pred, fig_index=2 * i + 2)
plot_qda_cov(qda, splot)
plt.axis('tight')
plt.suptitle('Linear Discriminant Analysis vs Quadratic Discriminant Analysis')
plt.show()