决策树/范例一: Decision Tree Regression
范例目的
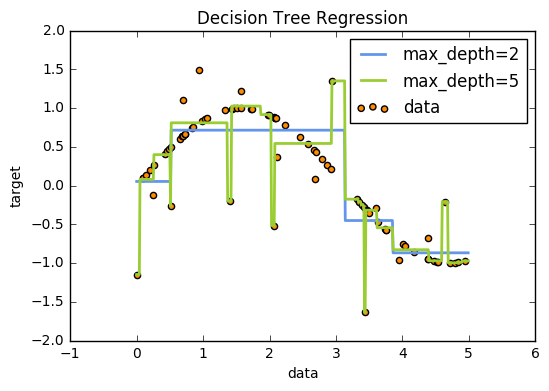
此范例利用Decision Tree从数据中学习一组if-then-else决策规则,逼近加有杂讯的sine curve,因此它模拟出局部的线性迴归以近似sine curve。 若决策树深度越深(可由max_depth参数控制),则决策规则越複杂,模型也会越接近数据,但若数据中含有杂讯,太深的树就有可能产生过拟合的情形。 此范例模拟了不同深度的树,当用带有杂点的数据可能造成的情况。
(一)引入函式库及建立随机数据资料
引入函式资料库
matplotlib.pyplot:用来绘製影像。sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor:利用决策树方式建立预测模型。
特徵资料
np.random():随机产生介于0~1之间的乱数RandomState.rand(d0,d1,..,dn):给定随机乱数的矩阵形状np.sort将资料依大小排序。
目标资料
np.sin(X):以X做为径度,计算出相对的sine值。ravel():输出连续的一维矩阵。y[::5] += 3 * (0.5 - rng.rand(16)):为目标资料加入杂讯点。
import numpy as np
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
rng = np.random.RandomState(1)
X = np.sort(5* rng.rand(80, 1), axis=0) #0~5之间随机产生80个数值
y = np.sin(X).ravel()
y[::5] += 3 * (0.5 - rng.rand(16)) #每5笔资料加入一个杂讯
(二)建立Decision Tree迴归模型
建立模型
DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth = 最大深度):DecisionTreeRegressor建立决策树回归模型。max_depth决定树的深度,若为None则所有节点被展开。此范例会呈现不同max_depth对预测结果的影响。
模型训练
fit(特徵资料, 目标资料):利用特徵资料及目标资料对迴归模型进行训练。
预测结果
np.arrange(起始点, 结束点, 间隔):np.arange(0.0, 5.0, 0.01)在0~5之间每0.01取一格,建立预测输入点矩阵。np.newaxis:增加矩阵维度。predict(输入矩阵):对训练完毕的模型测试,输出为预测结果。
regr_1 = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=2) #最大深度为2的决策树
regr_2 = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=5) #最大深度为5的决策树
regr_1.fit(X, y)
regr_2.fit(X, y)
X_test = np.arange(0.0, 5.0, 0.01)[:, np.newaxis]
y_1 = regr_1.predict(X_test)
y_2 = regr_2.predict(X_test)
(三) 绘出预测结果与实际目标图
plt.scatter(X,y):将X、y以点的方式绘製于平面上,c为数据点的颜色,label为图例。plt.plot(X,y):将X、y以连线方式绘製于平面上,color为线的颜色,label为图例,linewidth为线的宽度。
plt.figure()
plt.scatter(X, y, c="darkorange", label="data")
plt.plot(X_test, y_1, color="cornflowerblue", label="max_depth=2", linewidth=2)
plt.plot(X_test, y_2, color="yellowgreen", label="max_depth=5", linewidth=2)
plt.xlabel("data") #x轴代表data数值
plt.ylabel("target") #y轴代表target数值
plt.title("Decision Tree Regression") #标示图片的标题
plt.legend() #绘出图例
plt.show()
(四)完整程式码
print(__doc__)
# Import the necessary modules and libraries
import numpy as np
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Create a random dataset
rng = np.random.RandomState(1)
X = np.sort(5 * rng.rand(80, 1), axis=0)
y = np.sin(X).ravel()
y[::5] += 3 * (0.5 - rng.rand(16))
# Fit regression model
regr_1 = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=2)
regr_2 = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=5)
regr_1.fit(X, y)
regr_2.fit(X, y)
# Predict
X_test = np.arange(0.0, 5.0, 0.01)[:, np.newaxis]
y_1 = regr_1.predict(X_test)
y_2 = regr_2.predict(X_test)
# Plot the results
plt.figure()
plt.scatter(X, y, c="darkorange", label="data")
plt.plot(X_test, y_1, color="cornflowerblue", label="max_depth=2", linewidth=2)
plt.plot(X_test, y_2, color="yellowgreen", label="max_depth=5", linewidth=2)
plt.xlabel("data")
plt.ylabel("target")
plt.title("Decision Tree Regression")
plt.legend()
plt.show()